C# ARRAYS

Background
An array stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful to think of an array as a collection of variables of the same type stored at contigeous memory locations.

using System;namespace ConsoleApp1{class MyArray{static void Main(string[] args){int[] n = new int[10]; /* n is an array of 10 integers *//* initialize elements of array n */for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){n[i] = i + 100;}/* output each array element's value */foreach (int j in n){int i = j - 100;Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", i, j);i++;}Console.ReadKey();//Element[1] = 101//Element[2] = 102//Element[3] = 103//Element[4] = 104//Element[5] = 105//Element[6] = 106//Element[7] = 107//Element[8] = 108//Element[9] = 109}}}
Two-Dimensional Arrays
The simplest form of the multidimensional array is the 2-dimensional array. A 2- dimensional array is a list of one-dimensional arrays.
using System;namespace ConsoleApp1{class MyArray{public static void Main(string[] args){/* an array with 5 rows and 2 columns*/int[,] a = new int[5, 2] { { 0, 0 }, { 1, 2 }, { 2, 4 }, { 3, 6 }, { 4, 8 } };int i, j;/* output each array element's value */for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){for (j = 0; j < 2; j++){Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i, j]);}}Console.ReadKey();//a[0, 0]: 0//a[0, 1]: 0//a[1, 0]: 1//a[1, 1]: 2//a[2, 0]: 2//a[2, 1]: 4//a[3, 0]: 3//a[3, 1]: 6//a[4, 0]: 4//a[4, 1]: 8}}}
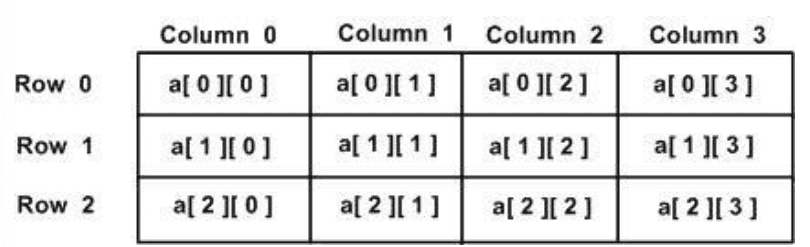
Jagged Arrays
A Jagged array is an array of arrays. You can declare a jagged array named scores:
using System;namespace ConsoleApp1{class MyArray{static void Main(string[] args){/* a jagged array of 5 array of integers*/int[][] a = new int[][] { new int[] { 0, 0 }, new int[] { 1, 2 }, new int[] { 2, 4 }, new int[] { 3, 6 }, new int[] { 4, 8 } };int i, j;/* output each array element's value */for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){for (j = 0; j < 2; j++){Console.WriteLine("a[{0}][{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i][j]);}}Console.ReadKey();//a[0][0]: 0//a[0][1]: 0//a[1][0]: 1//a[1][1]: 2//a[2][0]: 2//a[2][1]: 4//a[3][0]: 3//a[3][1]: 6//a[4][0]: 4//a[4][1]: 8}}}
Properties of the Array Class
The following table describes some of the most commonly used properties of the Array class
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| IsFixedSize | Gets a value indicating whether the Array has a fixed size. |
| IsReadOnly | Gets a value indicating whether the Array is read-only. |
| Length | Gets a 32-bit integer that represents the total number of elements in all the dimensions of the Array. |
| LongLength | Gets a 64-bit integer that represents the total number of elements in all the dimensions of the Array. |
| Rank | Gets the rank (number of dimensions) of the Array. |
Methods of the Array Class
The following table describes some of the most commonly used methods of the Array class:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear | Sets a range of elements in the Array to zero, to false, or to null, depending on the element type |
| Copy(Array, Array, Int32) | Copies a range of elements from an Array starting at the first element and pastes them into another Array starting at the first element. The length is specified as a 32-bit integer |
| CopyTo(Array, Int32) | Copies all the elements of the current one-dimensional Array to the specified one-dimensional Array starting at the specified destination Array index. The index is specified as a 32-bit integer. |
| GetLength | Gets a 32-bit integer that represents the number of elements in the specified dimension of the Array. |
| GetLongLength | Gets a 64-bit integer that represents the number of elements in the specified dimension of the Array. |
| GetLowerBound | Gets the lower bound of the specified dimension in the Array. |
| GetType | Gets the Type of the current instance. (Inherited from Object.) |
| GetUpperBound | Gets the upper bound of the specified dimension in the Array. |
| GetValue(Int32) | Gets the value at the specified position in the one-dimensional Array. The index is specified as a 32-bit integer |
| IndexOf(Array, Object) | Searches for the specified object and returns the index of the first occurrence within the entire one-dimensional Array |
| Reverse(Array) | Reverses the sequence of the elements in the entire one-dimensional Array |
| SetValue(Object, Int32) | Sets a value to the element at the specified position in the one-dimensional Array. The index is specified as a 32-bit int |
| Sort(Array) | Sorts the elements in an entire one-dimensional Array using the IComparable implementation of each element of the Array |
| ToStringk | Returns a string that represents the current object. (Inherited from Object.) |
Tags
Share
Table Of Contents
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff
Social Media
