Hash Table
April 26, 2024
1 min
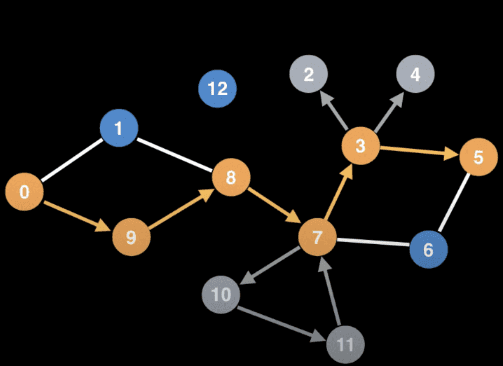
void dfs(int cur) {visited[cur] = true;for(int next: adjList[cur]) {if (visited[next] == false) {dfs(next);}}}visited = vector<bool>(n, false);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) if (!visited[i]) { dfs(i) };
void dfs(TreeNode cur) {if (cur == NULL) return;dfs(cur->left);dfs(cur->right);}
Thinking flow:
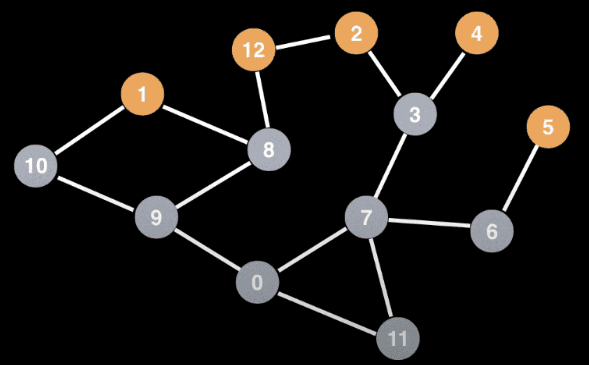
vector<vector<int>> adj; // adjacency list representationint n; // number of nodesint s; // source nodequeue<int> q;vector<bool> visited(n);q.push(s);visited[s] = true;while (!q.empty()) {int v = q.front();q.pop();for (int u : adj[v]) {if (!visited[u]) {visited[u] = true;q.push(u);}}}
Quick Links
Legal Stuff
Social Media