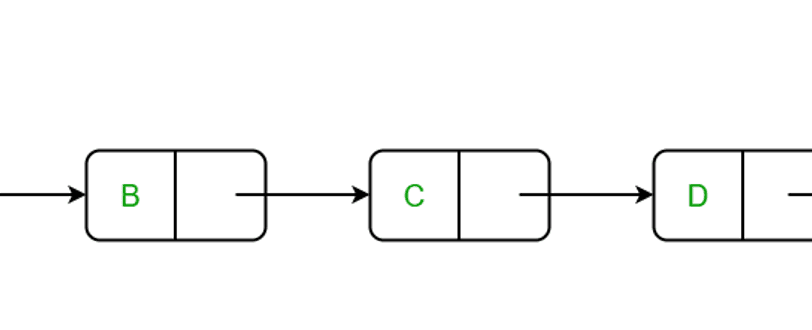
A series of nodes. each node contains 2 parts: information, a reference to the next node
Linked List vs. Array
- cannot randomly access
- size can grow or shrink at runtime
- memory allocation
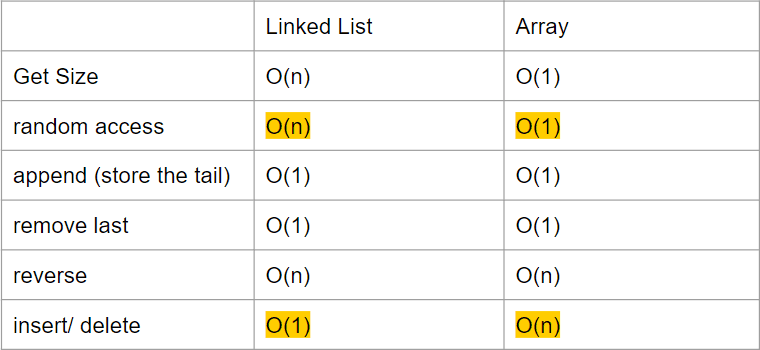 example
example
Use 2 pointers: slow and fast, initially pointing at the head.
- Let the fast pointer move twice as fast.
- When the fast pointer reaches the end of the linked list, the slow pointer is in the middle.
If there is no cycle: fast will reach the end of linked list => O(n)
If there is a cycle:
- At some point in time, both fast and slow will be in the cycle
- After that, the distance between them will decrease by 1 at a time (because fast move 2 steps
at a time, slow move 1 step at a time)
- So, let’s say the cycle has len K; fast and slow will be at the same node after K seconds.