Security

Hash vs Encrypt vs Encode
Hashing
- converting a given key into another smaller and fixed-size value: SHA-256, Bcrypt, MD5
- not reversible
- password storage, data’s integrity validation, Checksums
Encoding
- data is transformed from one form to other form. BASE64, ASCII, MP4
- reversible
- transform data into a form that is readable by external process
Encryption
- An encoding technique, in which message (text, json…) is encoded by encryption algorithm that only authorized people can read the message. RSA (Private key, public key)
- reversible
- transfer private data, authorization
Credential storage
- Plain Text
- if hacker can retrieve the database, they can extract password of users and use them for different sites engineer and Database admin can access the password
- Encrypted/Encode passwords (reversible)
Encrypt password by an encryption algorithm. (base64, rsa, …)
Hacker can register and know his password and the encrypted form => guess the encryption logic => decrypt all other passwords
- Hash password (not reversible)
Use hash function to hash the password before storing:
hash function is irreversible: choose the secure hash functions: SHA256, SHA512
avoid MD5, SHA1:
- high chance of collisions (2 diff keys => same value)
- big dictionary (21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc3)
risks:
- Select a password you think the victim has chosen (e.g.password1!, 123456, qwerty)
- Calculate the hash
- Compare the hash you calculated to the hash of the victim. If they match, you have correctly “cracked” the hash and now know the plaintext value of their password.
- Hash + Salt
- A salt is a unique, randomly generated string that is added to each password as part of the hashing process
- Salt is stored in database.
- Purpose:
- hacker has to crack hashes one at a time instead of calculating the hash once and compare with every stored hash. => slow hacking process
- impossible to check if 2 users have same password. hashed_password = hash(unique_salt + password)
- Hash + Salt + Pepper
- Pepper is a randomly generated string that is added to password as part of the hashing process.
- Similar to Salt, but:
- pepper is not stored in database. (env variable, secure centralized store)
- pepper is shared between all passwords rather than being unique like a salt.
- Purpose:
- prevent hacker from cracking any hash if they only have access to the database.
- Slow Hash + Salt + Pepper
- SHA-X hash is fast to compute => with a strong computer, hacker can brute force
- Use Slow Hash: bcrypt, scrypt
- they “slow down” its hashing speed => take very long time to brute force.
SSL/TLS
TLS - Transport Layer Security
- SSL => deprecated => now use TLS. a cryptographic protocol designed to provide communications security over a computer network. Part of HTTPS protocol
Before client and server can send and receive data securely using HTTPS, they need to do TLS handshake to verify each other and exchange necessary information.
TLS Handshake
- Client sends Client Hello message to Server which include:
- TLS version client supports (1.0 2.0 ..)
- cipher suites client supports (algorithm)
- a random bytes: client random
- Server sends Server Hello message to Client which include:
- Server’s SSL certificate
- server’s chosen cipher suites
- a random bytes: server random
- Client confirms Server’s identity (authentication) by checking the server’s SSL certificate using RSA encryption:
SSL certificate contains:
- domain name
- person/ organization owns the certificate
- which Certificate authority (CA) issued it
- CA’s digital signature
- issue date
- expiration date
- server’s PK (used later in key exchanges) …
The whole identity authentication is based on the idea “You trust the CA, and they trust me, therefore you can trust me.“:
- the browser has a build-in list of all CA’s public key
- it uses CA’s Public Key to decrypt the CA’s digital signature
- it confirms that the decrypted data is matched.
- Key Exchange, use RSA
- Client generates a random pre-master secret, encrypts it with the Server’s public key (found in Server SSL’s certificate), sends the result to Server
- Server decrypts the pre-master secret using its secret key.
- At this point, both Client and Server share the same pre-master secret.
- Both Client and Server generate session key from pre-master secret, client random, and server random
session_key = hash(pre-master secret, ClientHello.random, ServerHello.random)
Client is ready: The client sends a “finished” message that is encrypted with a session key.
Server is ready: The server sends a “finished” message encrypted with a session key.
The handshake is completed, and communication continues using symmetric encryption with key == session key
JWT
Json Web Token: an open standard that defines a way for securely transmitting data between parties (client, server). This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a secret or a public/private key pair using RSA.
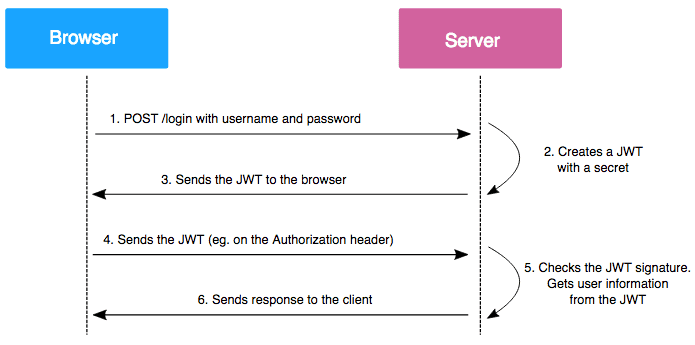
Usage: Authentication
Advantage:
- stateless: server does not need to maintain a session storage because all authentication information is stored in JWT, which is stored in client side (browser).
- because JWT is sent along with the request in the request header, it eliminates the possibility of CSRF (Cross-site Request Forgery) attack.
Disadvantage:
- JWT only becomes invalid when it expires. The user has no built-in feature to revoke the validity of a token explicitly
- The solution would be to create a database to maintain a revocation list. This would add complexity to the system and eliminate the stateless property of JWT authentication.
SOP - CORS
SOP
“A web application using APIs can only request HTTP resources from the same origin the application was loaded from.” a policy that is compiled by most of the browsers (for security reason)
- not apply for debug tools like Postman
- not apply for some html tags:
<script><img><link><frame>, <iframe>
CORS
- CORS is a mechanism to bypass SOP.
- Example: frontend app served from https://example.com call APIs to backend app served from https://api.example.com.
- Using CORS, we can define which origin can request the server’s origin
SQL injection
SQL injection is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to interfere with the queries that an application makes to its database
How to prevent?
use Prepared Statement: database to distinguish between code and data, regardless of what user input is supplied.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff
Social Media
