System Design Guideline

Step 1: Requirement clarification
Purpose: to solve the RIGHT problem!
- Functional requirements
- What specific features are we going to build?
- How many users daily does the product have?
- Can I assume the read/write ratio is x:y? 100:1, 10:1
- Does the system needs to be highly available, or do we focus on consistency? (CAP)
- What is the required latency? => p99 <= 100ms
Interview Question: Design URL shortener. (https://tinyurl.com/app)
Q: Can you tell me more about the specific features we need to support?
A: Given a URL, our service should generate a shorter and unique alias.
Q: How short the shortened link should be?
A: It is up to you.
Q: Does the shortened link have an expiration time?
A: Users can specify it.
Q: Can user pick their shortened URL?
A: Nope.
Q: Does URL need to be random? A: Yes, it should not be guessable Q: What are the non-functional requirements regarding availability, latency, and throughput? A: It should be real-time (low latency) and highly available. You can assume 500M new URLs per month. Q: What is the read: write ratio? A: read:write = 100:1
Step 2: Estimation
Purpose: estimate the scale of our system
- Throughput (QPS)
- Storage (Database, 10GB …)
- Cache (RAM memory)
We don’t need to get the correct answer when estimating the system capacity, just a rough estimation.
Example: URL shortener
500M new URL / month => 200 url/s
Read/Write = 100:1
Step 3: Design API
POST api/v1/shortenrequest param:{ longURL: string}response: {shortURL: string}GET api/v1/{shortURL}status code: 301 (redirect)response: longURL
Step 4: Database & Data model
Database
- Choose between SQL and NoSQL. Draft the data model. (i.e define schema)
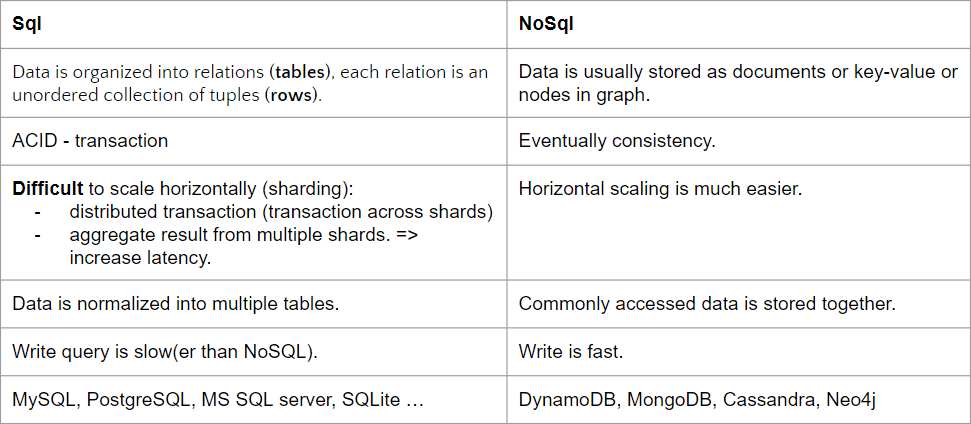
- How to choose?
- If the system requires high consistency (e.g, banking system, order, wallet …) => SQL
- If we can sacrifice consistency (i.e, data can be stale) and there is a lot of data => NoSQL
- If data in system is independent => NoSQL (log, time series data (Stock price), URL shortener)
- If you don’t have a decent reason to choose NoSQL, go with SQL by default.
Data model
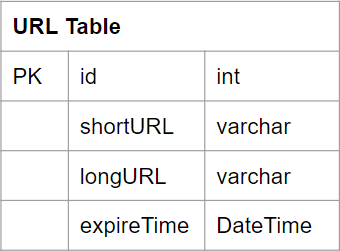
Step 5: High-level design and Deep dive
- Define the flow.
- Draw the high level design (draw.io)
- Choose the correct algorithms & data structures (e.g: QuadTree, Geohash, Consistent Hashing …)
- Deep dive into how to scale, eliminate SPoF
Flow:
- Write flow: given a longURL => we use a hash function to get the shortURL => store to DB with expire date.
- Read flow: given a shortURL, we fetch from cache:
if cache hit, return longURL
else query from DB
if the URL is expired, return error.
else write back to cache and return.
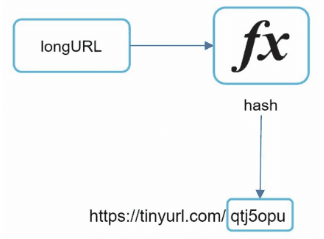
How to choose Hash Function?
> shortURL contains [a-z, A-Z, 0-9] ~ 62 characters.> We need to store 60 billions URL for 10 years.> => shortURL length should be 7 characters. Because 62^6 < 60B < 62^7> We have few options here: (again, explain the tradeoff to interviewer)> - Pick the first 7 characters of the hash => maybe leads to collision.> - Pick the first 7 characters and query the database to check collision. => high latency.> - Randomly pick 7 character from the hash
Other approaches:
> Use encoding instead of hashing> Generate an unique id integer for each longURL> Convert to base62> - Pros: no collision because the id is unique> - Cons: need to build a distributed ID generator, which is hard.
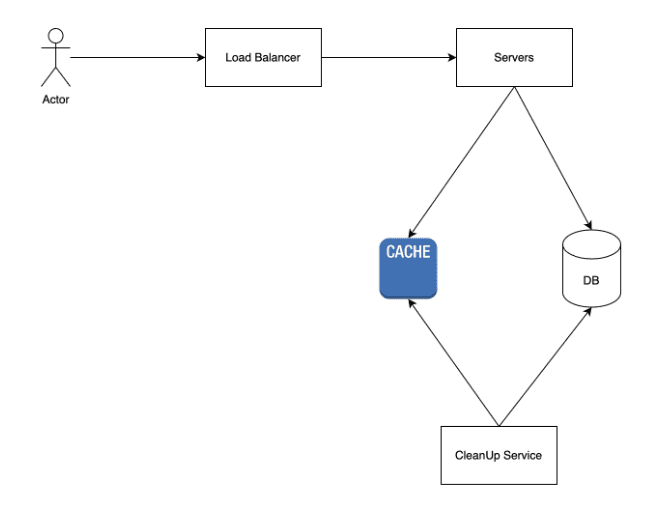
Make it scalable and reliable.
- Use multiple servers to serve the client => improve reliability, increase qps …
- Use a Load Balancer to distribute the traffic: Round robin, Consistent Hashing …
- Use a Cache to reduce the latency; 20/80 rule => cache only 20% of data.
Prepare some common systems:
- Design ID generator
- Design rate limiter
- Design notification system
- Design order system
- Design Twitter news feed
- Design Proximity service (find nearby restaurants, drivers, atm, hotel …)
Tags
Share
Table Of Contents
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff
Social Media
