WPF Basic Concepts

What is WPF?
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF)
- is a
graphical subsystem by Microsoftfor rendering user interfaces in Windows-based applications. - It is part of the
.NET Frameworkand provides a consistent programming model forbuilding applicationswith visually stunning user experiences.
What are the main features of WPF?
The main features of Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) include:
- Declarative Programming with
XAML:
- WPF uses XAML (eXtensible Application Markup Language) to
define the user interfacein a declarative way. XAML separates the UI design from business logic, enabling better collaboration between designers and developers.
- Rich
Media Support:
- WPF supports various media types, including vector graphics,
bitmap images, audio, and video. - It allows for the creation of visually rich and interactive applications.
Data Binding:
- WPF provides robust data-binding capabilities, enabling
automatic synchronizationbetween the UI and the underlying data. - Supports binding to different data sources, including databases, XML, and custom objects.
- Accessibility and
Localization:
- WPF includes features to support accessibility, making applications usable by people with disabilities.
- Provides localization support, enabling applications to be adapted for different languages and cultures.
Explain the architecture of WPF.
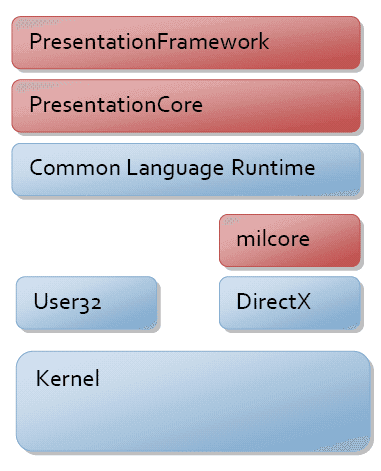
- PresentationCore:
- This assembly provides the foundational types for the WPF graphics system, including basic
elements, animation, and visual trees. It handles core presentation functionality.
- PresentationFramework:
- This assembly contains higher-level classes that define the WPF control model, styles, and data binding.
It is built on
top of PresentationCoreand provides controls likebuttons, text boxes, and other UI elements.
- Milcore:
- Milcore (Media Integration Layer Core) handles the
rendering of graphics. It is written in unmanaged code for performance reasons and works closelywith DirectX to render graphics. - WPF uses DirectX for rendering
2D and 3D graphics. DirectX provides hardware acceleration, which enhances the performance of graphics rendering.
What is XAML? How is it used in WPF?
What is XAML?
XAML (Extensible Application Markup Language) is a declarative XML-based language developed by Microsoft.
It is primarily used for initializing structured values and objects in application development.
How is it used in WPF?
In Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF), XAML is used extensively to define the user interface (UI) of
an application. WPF leverages XAML for its powerful layout capabilities, styling, data binding, and more.
Here’s how XAML is used in WPF:
Defining the UI Layout: XAML provides a way to define the structure and layout of the UI elements. This includes arranging controls such as
buttons, text boxes, labels, and more within containers likegrids, stacks, and canvases.Event Handling: XAML allows you to attach event handlers to UI elements. These event handlers are then implemented in the
code-behind file.Styling and Templates: XAML supports styles and templates, which help in defining the look and feel of the UI elements. Styles can be used to set properties on multiple controls, while templates define the visual structure of controls.
Data Binding: XAML supports data binding, enabling the UI elements to bind to data sources like objects, lists, and databases. This is a powerful feature for creating dynamic and interactive applications.
Animations and Storyboards: XAML provides support for animations and storyboards, allowing developers to create rich, animated user experiences.
Resources: XAML allows you to define resources, such as brushes, styles, and control templates, which can be reused throughout the application.
MainWindow.xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfApp.MainWindow"xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"Title="MainWindow" Height="200" Width="400"><Grid><StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center"><TextBox Name="inputTextBox" Width="200" Margin="10"/><Button Content="Click Me" Width="200" Click="Button_Click" Margin="10"/><TextBlock Name="outputTextBlock" Width="200" Margin="10"/></StackPanel></Grid></Window>
MainWindow.xaml.cs
using System.Windows;namespace WpfApp{public partial class MainWindow : Window{public MainWindow(){InitializeComponent();}private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e){outputTextBlock.Text = $"Hello, {inputTextBox.Text}!";}}}
Describe the difference between WPF and WinForms.
WPF (Windows Presentation Foundation) and WinForms (Windows Forms) are both UI frameworks for building Windows applications, but they have significant differences in terms of design, capabilities, and underlying architecture. Here’s a comparison of the two:
- Framework Basis
WPF (Windows Presentation Foundation):
- Based on
DirectXfor rendering, which provides better graphics and performance for modern applications. - Uses
XAML(Extensible Application Markup Language) for designing UI, which separates UI design from business logic.
- Based on
WinForms (Windows Forms):
- Uses
GDI+(Graphics Device Interface) for rendering. - UI design is typically done directly in C# or VB.NET, with a drag-and-drop interface in Visual Studio.
- Uses
- Data Binding and MVVM Pattern
WPF:
- Strong support for data binding and the
MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel) pattern, which promotes a clean separation of concerns. - Allows for more reusable and testable code.
- Strong support for data binding and the
WinForms:
- Basic data binding support, generally using the traditional event-driven programming model.
- Does not natively support MVVM; developers typically use
MVC(Model-View-Controller) or MVP (Model-View-Presenter) patterns.
Summary
- WPF is better
suited for applications that require modern, rich, and complex UIswith extensive customizations and data binding. - WinForms is ideal for
simpler, traditional desktop applicationswhere rapid development and ease of use are more critical.
Tags
Share
Table Of Contents
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff
Social Media
